In this article, I will show you how to create a custom middleware in asp.net core and show you the difference between
Use and Map. By the end of this article, you will learn the following thing.- How to create custom middleware in asp.net core
- When to use
UseandMap. - How to conditionally register middleware with a real-world example.
Request pipeline middleware
.Run()
Delegates terminate the request pipeline
.Use()
Multiple request delegates can be chained
.Map()
The map is used for conditional branching the request based on the path,
Steps To Create MiddleWare
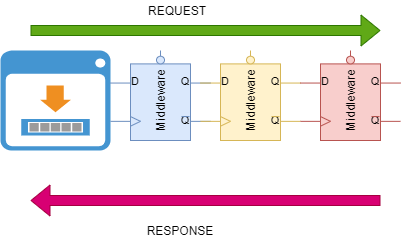
Middleware are created once per application lifetime
- public constructor with
RequestDelegateparameter - Public method
InvokeorInvokeAsync- The first Parameter must be
HttpContext - Must return Task
- Additional arguments can be injected
- The first Parameter must be
void Main()
{
CreateWebHostBuilder(new string[] { "" }).Build().Run();
}
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup<Startup>();
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ValuesController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<string>> Get()
{
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
}
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_3_0);
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseCors();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute("default", "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}");
});
}
}
Let’s understand Map and Use with examples. Go to the Configure method in the startup.cs file and add Map and Use. If you run the application and hit the localhost:5000/v1, it will print the Map will terminate the pipeline and terminate the pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Map will terminate the pipeline");
});
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("It will not execute");
await next.Invoke();
});
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseCors();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute("default", "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}");
});
}
If you change the order of means, the Use above the Map will print both the messages.
Map
The convention for branching the pipeline is to use map extensions. The Map extension method is used to find request delegates depending on the path of a request.
app.Map("/v1", branchPipeLine =>
{
branchPipeLine.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Execute v1");
});
});
app.Map("/v2", branchPipeLine =>
{
branchPipeLine.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Execute v1");
});
});
Conditionally Add MiddleWare using Map
Let’s understand this with one example. There are two paths, /v1 and /v2In the following example. If the user hits the /v1 path, he will not get any cors error, but if the user hits the /v2 path, then he will get a cors error because CORS middleware is not registered in the /v2 path,
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.Map("/v1", branchPipeLine =>
{
branchPipeLine.UseStaticFiles();
branchPipeLine.UseRouting();
branchPipeLine.UseCors(policy =>
{
policy.AllowAnyOrigin();
});
branchPipeLine.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute("default", "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}");
});
});
app.Map("/v2", branchPipeLine =>
{
branchPipeLine.UseStaticFiles();
branchPipeLine.UseRouting();
branchPipeLine.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute("default", "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}");
});
});
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', (event) => {
console.log("DOM Loaded");
fetch("http://localhost:5000/v2/api/values")
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
