Web application security is very crucial because attacks against web apps are the top cause of data breaches. Business /company need security to protect their data and assets.
Many developers confused between hashing and encryption. If you ask where to protect the user password, their first reaction will encrypt the password. But the right solution is to hash the password with some random salt.
Why hashing the password not the encryption
Hashing is a one-way process that means it cannot get back the original password from the calculated hash. The only way to verify is that compute the hash of the password and compare it with the hash password.
Encryption is two process means you can encrypt the data and decrypt back with the key. If the key is compromised, then data breach will happen.
What is salt in hashing
Salt is random data that is used as an additional input to one way hash function. They are used for the following reason
-
Used to safeguard passwords in storage
-
Salts defend against a pre-computed hash attack, e.g. rainbow tables.
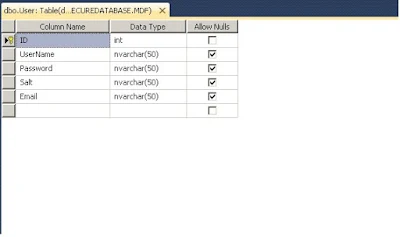
In this post, I will show you how to hash user password in ASP.N ET. Before going into implementation details, let first design the table structure. For the sake of simplicity, I have taken only some fields.
Right-click on the website, add ASP.NET special folder App_Code. Then Right-click again on App_Code folder and add new item Linq to SQL classes and drag the table from Server Explorer to Linq to SQL classes surface.
Again right click on App_Code and add new class named UserManager.cs inside App_Code folder.Now paste the following code in it
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Web.Security;
public class UserManager
{
private static string CreateSalt(int size)
{
//Generate a cryptographic random number.
RNGCryptoServiceProvider rng = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider();
byte[] buff = new byte[size];
rng.GetBytes(buff);
// Return a Base64 string representation of the random number.
return Convert.ToBase64String(buff);
}
public static string CreatePasswordHash(string pwd, string salt)
{
string saltAndPwd = String.Concat(pwd, salt);
string hashedPwd =FormsAuthentication.HashPasswordForStoringInConfigFile(saltAndPwd, "sha1");
return hashedPwd;
}
public void CreaetUser(string userName, string password, string email)
{
SecureLoginDataContext dc = new SecureLoginDataContext();
string salt = CreateSalt(8);
User user = new User();
user.Email = email;
user.Salt = salt;
user.Password = CreatePasswordHash(password, salt);
user.UserName = userName;
dc.Users.InsertOnSubmit(user);
dc.SubmitChanges();
}
public static User GetUserDetails(string username)
{
SecureLoginDataContext dc = new SecureLoginDataContext();
User result = (from c in dc.Users
where c.UserName.Equals(username)
select c).FirstOrDefault();
return result;
}
}
Add three new pages to your website named Login.aspx,Welcome.aspx and Registration.aspx Open Login.aspx and add following code in it Login.aspx
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="Login.aspx.cs" Inherits="Login" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.style1
{
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<table class="style1">
<tr>
<td>
UserName</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtUserName" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Password</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtPassword" runat="server" TextMode="Password" Width="128px"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
</td>
<td>
<asp:Button ID="btnLogin" runat="server" Text="Login"
onclick="btnLogin_Click" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
<p>
<a href="Registration.aspx">Not a registred member</a></p>
</body>
</html>
Login.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class Login : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void btnLogin_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
User user = UserManager.GetUserDetails(txtUserName.Text);
string tempHashPassword = UserManager.CreatePasswordHash(txtPassword.Text, user.Salt);
//Compare tempHashPassword with haspassword stored in database.
if (tempHashPassword == user.Password)
{
Response.Redirect("Welcome.aspx");
}
else
{
Response.Write("Invalid username/password");
}
}
}
Open Registration.aspx and add following code in it
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="Registration.aspx.cs" Inherits="Registration" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.style1
{
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<table class="style1">
<tr>
<td>
UserName</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtUserName" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Password</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtPassword" runat="server" TextMode="Password"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Email</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtEmail" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
</td>
<td>
<asp:Button ID="btnCreate" runat="server" onclick="btnCreate_Click"
Text="Create" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Registration.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class Registration : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void btnCreate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UserManager user = new UserManager();
user.CreaetUser(txtUserName.Text, txtPassword.Text, txtEmail.Text);
Response.Redirect("Login.aspx");
}
}